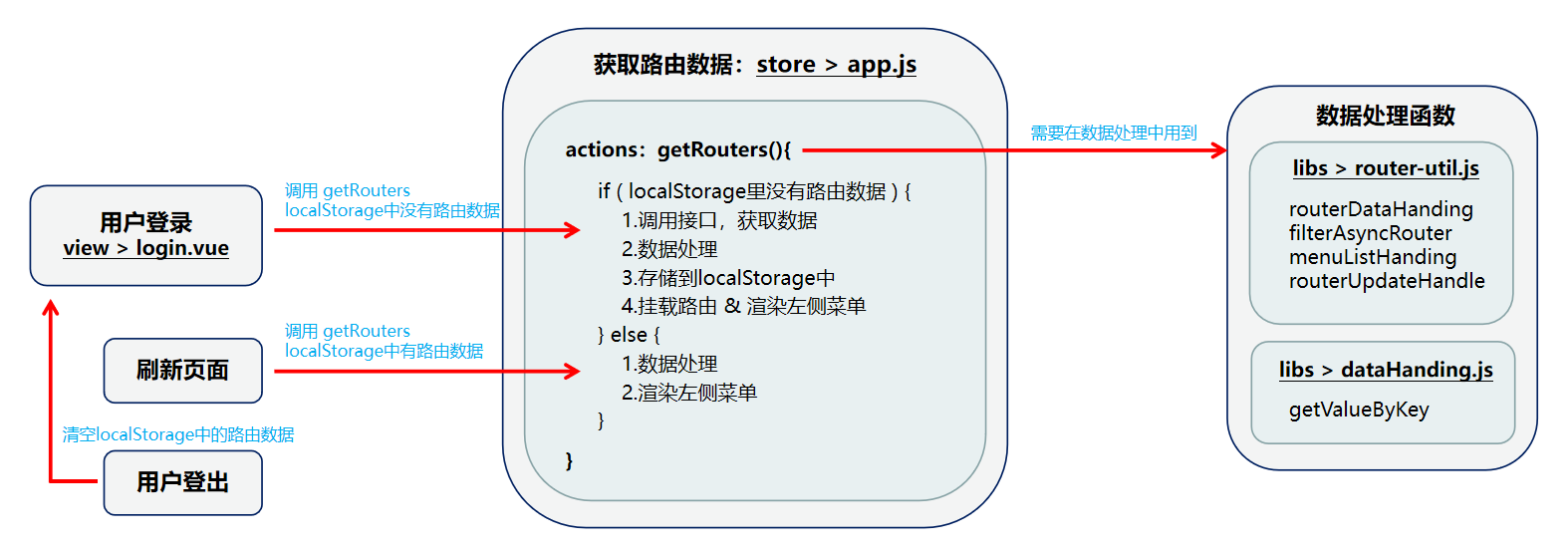
# 路由数据处理
路由数据处理、路由改造、菜单渲染 是整个开发步骤的核心部分。路由数据处理 时,需要开发者理清其完整的思路,同时需封装多个方法:
- store > module > app.js / 完整代码 →
- view > login > login.vue / 完整代码 →
- libs > router-util.js / 完整代码 →
- libs > dataHanding.js > arraySort() / 完整代码 →
- libs > tools.js > lazyLoadingCop() / 完整代码 →
- store > module > user.js / 完整代码 →
# store > module > app.js
# actions 追加 getRouters,获取动态路由数据:
import { getAllMenus } from "@/api/data";// 获取全部路由数据
// 获取动态路由数据
getRouters({ commit, rootState }, routes) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
var gotRouter = []; // 设置动态路由
if (localRead("dynamicRouter-template") === "") {
/* localStorage里dynamicRouter值为空 -> 没有路由数据 -> 获取路由数据 */
console.log("获取路由:从api");
try {
getAllMenus(rootState.user.token)
.then(res => {
console.log(res); // 从api获取到的路由数据
... // 接下来做路由数据处理
})
.catch(err => {...});
} catch (error) {...}
} else {
/* 有路由数据 -> 直接从localStorage里面获取 */
console.log("获取路由:从localStorage");
... // 接下来做路由数据处理
}
});
}
# view > login > login.vue
# handleSubmit 方法微调, getUserInfo 拉取用户数据后,异步调用 vuex 的 getRouters 方法
methods: {
...mapActions(["handleLogin", "getUserInfo", "getRouters"]),
handleSubmit({ userName, password }) {
this.handleLogin({ userName, password }).then(res => {
res.data.status === 200 && // 登录成功返回200,才调用 getUserInfo 方法
this.getUserInfo().then(res => {
this.getRouters().then(resRoutes => { // 调用 getRouters 方法
this.$router.push({ name: this.$config.homeName });
});
});
});
}
}
此时我们在 用户登录 后,可以获取动态路由的 api接口数据:
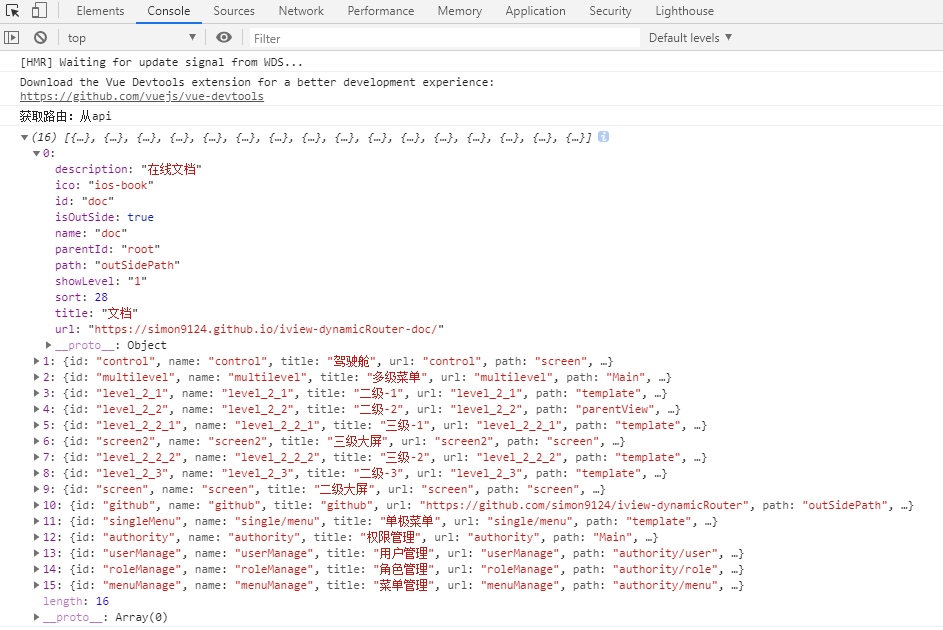
我们需要做 数据处理,将获取到的 api接口数据 转化成系统可识别的 路由数据:
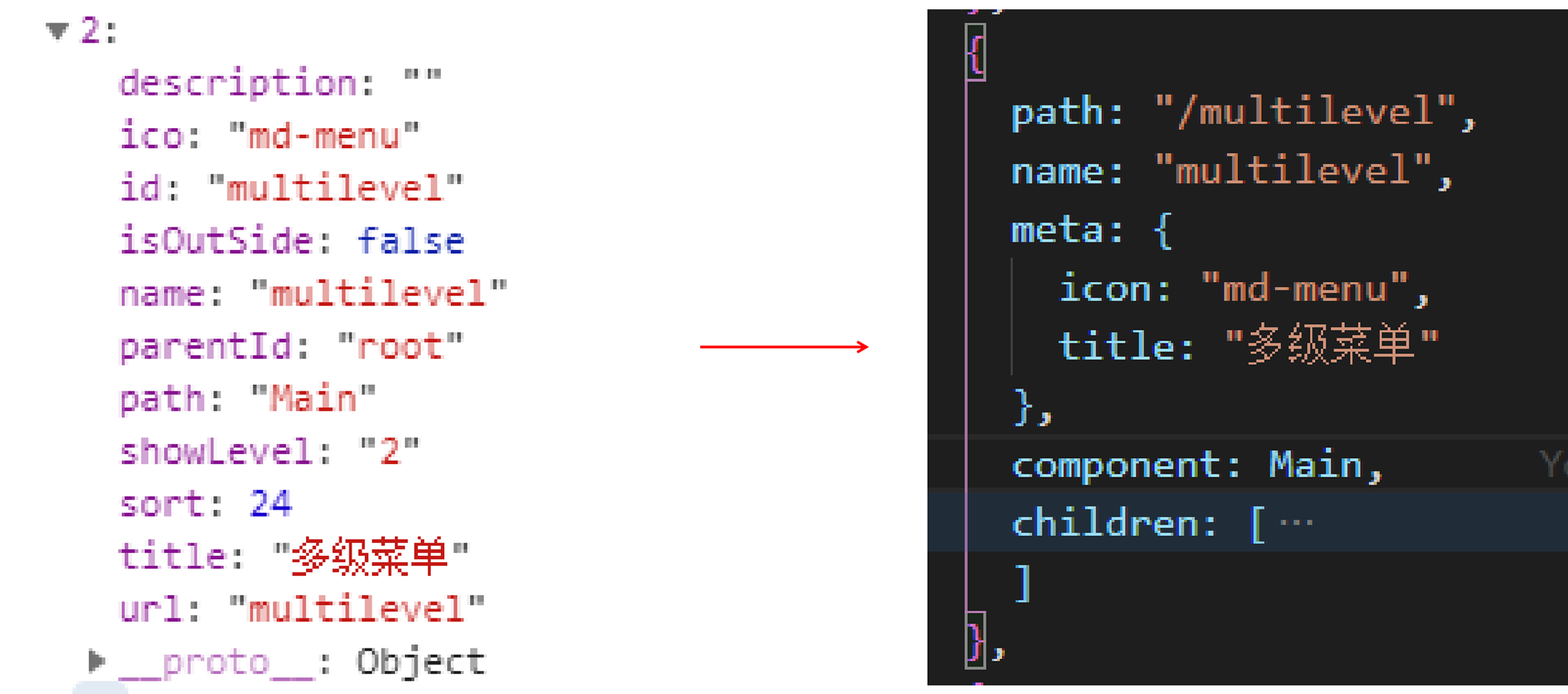
# libs > router-util.js
# 1.函数 routerDataHanding:遍历动态路由的 api接口数据,转为路由基础数据
// @函数:遍历后台传来的路由数据,转为路由基础数据
export const routerDataHanding = (apiRouterData) => {
const asyncRouterMap = []
/* 1.路由挂载 */
// 1-1.根节点
...
// 1-2.非根节点 - 递归
...
/* 2.路由处理 */
// 递归:1.处理sort排序(后端排序可忽略);2.处理重定向
...
return asyncRouterMap
}
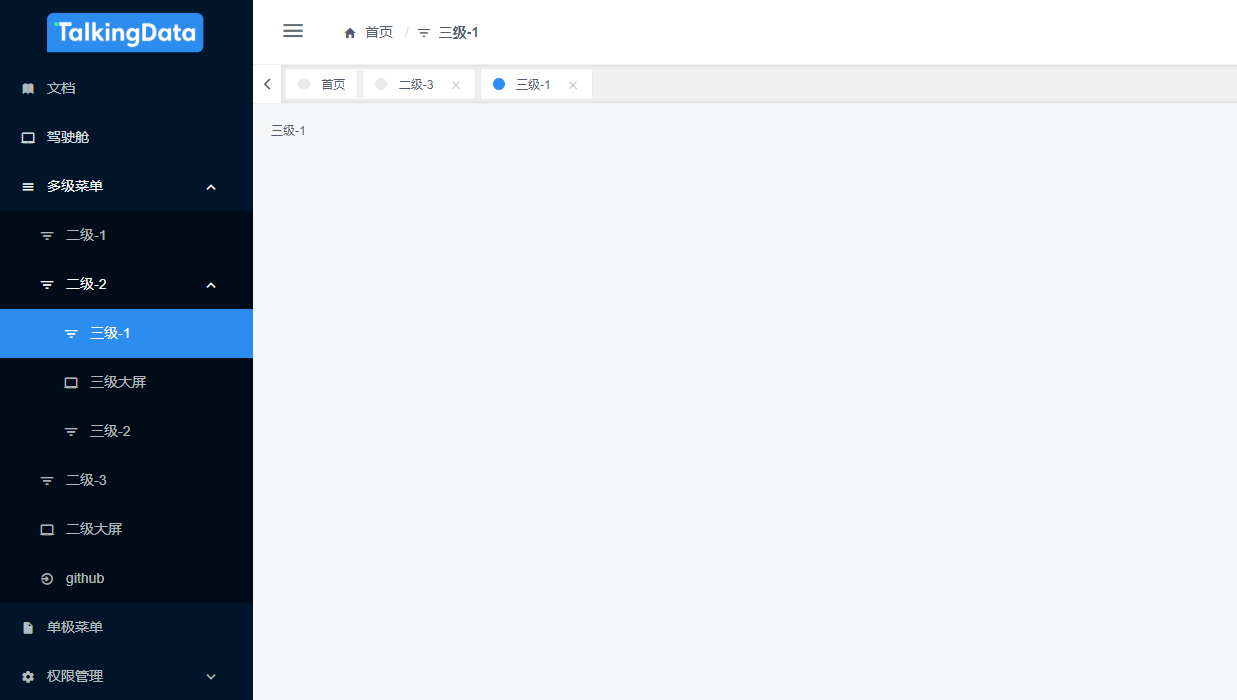
- 1-1 各类
路由-菜单的挂载方式
| 外链 | Main 组件内 | 菜单位置 | 类型 | component | 参考页面 | 路由 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 是 | —— | 根节点/子节点 | 链接 | —— | 文档、 github | 外链路由 |
| 否 | 否 | 根节点/子节点 | 页面 | 组件路径 | 驾驶舱、二级大屏、三级大屏 | 大屏路由 |
| 否 | 是 | 根节点 | 模块 | Main | 多级菜单、权限管理 | 父级路由 |
| 否 | 是 | 子节点 | 模块 | parentView | 二级-2 | 父级路由 |
| 否 | 是 | 子节点 | 页面 | 组件路径 | 二级-1、三级-1 等 | 子级路由 |
- 1-2 路由挂载 - 根节点:根据
parentId为root判断,再根据isOuside、path等字段创建不同的路由结构
路由挂载 - 根节点
apiRouterData.forEach((route) => {
if (route.parentId === 'root') {
if (route.isOutSide === true) {
// 外链,菜单显示该页面选项, -> 根据url创建外链路由
asyncRouterMap.push({
path: route.path,
name: route.name,
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
href: route.url,
id: route.id, // 根据id确定子组件
},
sort: route.sort, // 排序用
children: [],
})
} else if (route.path === 'Main') {
// 非外链,有子节点的父级路由(模块,非页面)-> 创建父结构路由
asyncRouterMap.push({
path: route.url === '/' ? route.url : '/' + route.url,
name: route.name,
component: 'Main',
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
hideInBread: true,
id: route.id, // 根据id确定子组件
},
sort: route.sort, // 排序用
children: [],
})
} else if (parseInt(route.showLevel) === 2) {
// 非外链,无子节点,页面含菜单栏,菜单显示该页面选项 -> 创建父子结构路由
asyncRouterMap.push({
path: '/' + route.url.split('/')[0],
name: route.name.split('/')[0],
component: 'Main',
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
hideInBread: true,
id: route.id,
},
sort: route.sort, // 排序用
children: [
{
path: route.url
.split('/')
.filter((val, index) => {
return index !== 0
})
.join('/'),
name: route.name
.split('/')
.filter((val, index) => {
return index !== 0
})
.join('/'),
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
id: `_${route.id}`,
},
component: route.path,
children: [],
},
],
})
} else {
// 非外链,无子节点,页面不含菜单栏 -> 根节点路由,与main组件平级
asyncRouterMap.push({
path: '/' + route.url,
name: route.name,
component: route.path,
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
hideInBread: true,
hideInMenu: parseInt(route.showLevel) !== 1, // true or false 菜单是否隐藏该页面选项,
id: route.id, // 根据id确定子组件
},
sort: route.sort, // 排序用
children: [],
})
}
}
})
- 1-3 路由挂载 -非根节点:需递归,其他同根节点,根据不同字段创建不同的路由结构
路由挂载 - 非根节点
const handleRecurrence = (recurrenceData) => {
recurrenceData.forEach((data) => {
apiRouterData.forEach((route) => {
// 根据 parentId 找寻其父级路由
if (data.meta.id === route.parentId) {
if (route.isOutSide === true) {
// 外链 -> 根据url创建外链路由
data.children.push({
path: route.path,
name: route.name,
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
href: route.url,
id: route.id, // 根据id确定子组件
},
sort: route.sort, // 排序用
children: [],
})
} else if (route.path === 'parentView') {
// 非外链,有子节点的二级父级路由(模块,非页面)-> 创建父结构路由
data.children.push({
path: route.url === '/' ? route.url : '/' + route.url,
name: route.name,
component: 'parentView',
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
hideInBread: true,
id: route.id, // 根据id确定子组件
},
sort: route.sort, // 排序用
children: [],
})
} else if (parseInt(route.showLevel) === 2) {
// 非外链,页面含菜单栏,菜单显示该页面选项 -> 创建子路由
data.children.push({
path: route.url,
name: route.name,
component: route.path,
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
id: route.id, // 根据id确定子组件
},
sort: route.sort, // 排序用
children: [],
})
} else {
// 非外链,页面不含菜单栏,菜单显示该页面选项 -> 根节点路由,与 main 组件平级(暂时为根菜单)
// 在app.js里调用 menuListHanding 方法,将原本不是根菜单的数据重新挂载到相应位置
asyncRouterMap.push({
path: '/' + route.url,
name: route.name,
component: route.path,
meta: {
icon: route.ico,
title: route.title,
hideInBread: true,
hideInMenu: parseInt(route.showLevel) !== 1, // true or false 菜单是否隐藏该页面选项
parentId: route.parentId,
notInMenu: true, // 追加notInMenu字段,为了将原本不是根菜单的数据重新挂载到相应位置
id: route.id,
},
sort: route.sort, // 排序用
children: [],
})
}
}
})
// console.log(data);
handleRecurrence(data.children)
})
}
handleRecurrence(asyncRouterMap)
- 1-4 路由处理:处理
sort排序(后端排序可忽略); 处理重定向
import { arraySort } from '@/libs/dataHanding' // 对象数组根据key排序
const handleData = (routeData) => {
routeData.sort(arraySort('sort', 'desc')) // sort排序,后端排序可忽略
routeData.forEach((route) => {
// 有子组件
if (route.children.length !== 0) {
// 1.子组件sort排序,后端排序可忽略
route.children.sort(arraySort('sort', 'desc'))
// 2.重定向为第一个非模块菜单的子组件
for (let i = 0; i < route.children.length; i++) {
if (route.children[i].children.length === 0) {
route.redirect = route.path + '/' + route.children[i].path
break
}
}
}
handleData(route.children) // 递归
})
}
handleData(asyncRouterMap)
- 1-5 在 app.js 的
getRouters中调用routerDataHanding方法,得到处理后的路由数据,并将这个数据存到localStorage
import { routerDataHanding } from '@/libs/router-util' // 遍历后台返回的路由数据,转为路由基础数据
if (localRead("dynamicRouter-template") === "") {
/* localStorage里dynamicRouter值为空 -> 没有路由数据 -> 获取路由数据 */
console.log("获取路由:从api");
try {
getAllMenus(rootState.user.token)
.then(res => {
var routerData = res.data.data; // 从api获取到的路由数据
routerData = routerDataHanding( // 调用 routerDataHanding 做路由数据处理
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(routerData))
);
localSave("dynamicRouter-template", JSON.stringify(routerData)); // 存储routerData到localStorage
console.log("处理后的路由数据:", routerData);
...
})
.catch(err => {...});
} catch (error) {...}
} else {
/* 有路由数据 -> 直接从 localStorage 里面获取 */
console.log("获取路由:从localStorage");
console.log("localStorage 里的路由数据:", JSON.parse(localRead("dynamicRouter-template")));
}
此时我们在 用户登录 或 登录后刷新页面 ,可以获取 数据处理处理后的动态路由:
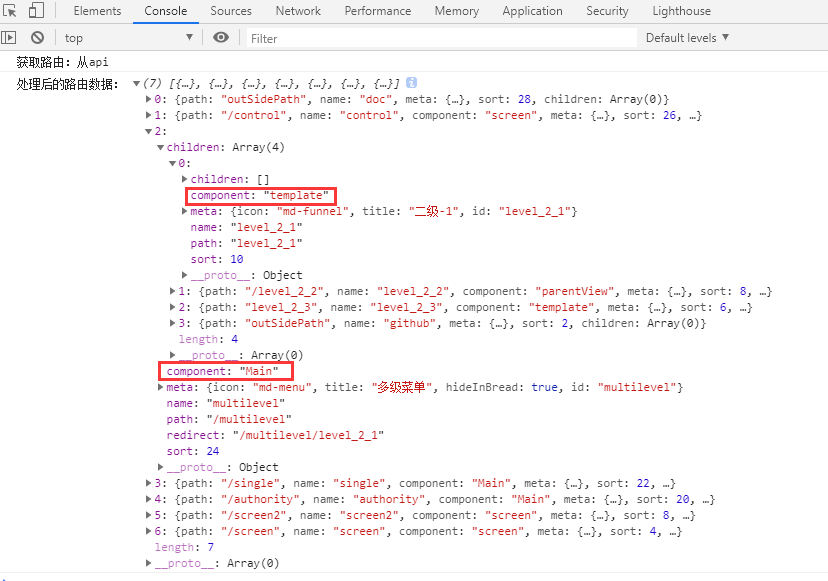
数据处理并未结束
此时数据已经大体符合路由格式,但是 component——组件 字段是字符串,我们需要将其转换为真正的 前端组件对象,方能真正符合路由数据格式。
# 2.函数 filterAsyncRouter:遍历路由基础数据,转为 前端组件对象
import { lazyLoadingCop } from '@/libs/tools' // 引入组件
// @函数: 遍历路由基础数据,转换为前端组件对象
export const filterAsyncRouter = (asyncRouterMap) => {
const accessedRouters = asyncRouterMap.filter((route) => {
if (route.component) {
if (route.component === 'Main') {
route.component = Main // Main组件特殊处理
} else if (route.component === 'parentView') {
route.component = parentView // parentView组件特殊处理
route.meta.hideInBread = true // 还有子路由因此不显示在面包屑
} else {
route.component = lazyLoadingCop(route.component)
}
}
if (route.children && route.children.length) {
route.children = filterAsyncRouter(route.children) // 子组件递归
}
return true
})
// console.log(accessedRouters);
return accessedRouters
}
- 在 app.js 的
getRouters中调用filterAsyncRouter方法,路由数据处理后转换为前端组件对象
import {
routerDataHanding, // 遍历后台返回的路由数据,转为路由基础数据
filterAsyncRouter, // 遍历路由基础数据,转换为前端组件对象
} from '@/libs/router-util'
getRouters({ dispatch, commit, rootState }, routes) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
var gotRouter = []; // 设置动态路由
if (localRead("dynamicRouter-template") === "") {
/* localStorage里dynamicRouter值为空 -> 没有路由数据 -> 获取路由数据 */
console.log("获取路由:从api");
try {
getAllMenus(rootState.user.token)
.then(res => {
var routerData = res.data.data; // 从api获取到的路由数据
routerData = routerDataHanding( // 调用 routerDataHanding 做路由数据处理
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(routerData))
);
localSave("dynamicRouter-template", JSON.stringify(routerData)); // 存储 routerData 到 localStorage
gotRouter = filterAsyncRouter(routerData); // 过滤路由,路由组件转换
console.log("转换成组件后的路由数据:", gotRouter);
...
})
.catch(err => {...});
} catch (error) {...}
} else {
/* 有路由数据 -> 直接从 localStorage 里面获取 */
console.log("获取路由:从localStorage");
gotRouter = filterAsyncRouter(
JSON.parse(localRead("dynamicRouter-template"))
);
console.log("转换成组件后的路由数据:", gotRouter);
...
}
});
}
这回再看看 用户登录 或 登录后刷新页面 的 经数据处理并转换为前端组件的路由数据:
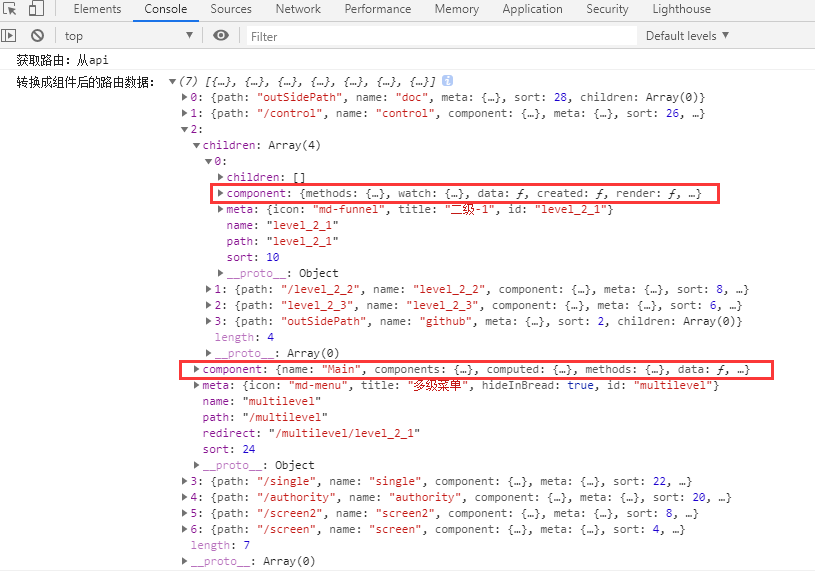
数据处理告一段落
此时终于符合路由格式,数据处理告一段落。看似很复杂,梳理好逻辑又很清晰;看似没什么页面变化,实则代码波涛汹涌...
# libs > dataHanding.js
/**
* 按照对象数组[{},{},{}...]的某个object key,进行数组排序
* @param {String} key 要排序的key
* @param {String} sort 正序/倒序:asc/desc,默认为asc
*/
export function arraySort(key, sort) {
return function (a, b) {
if (sort === 'asc' || sort === undefined || sort === '') {
// 正序:a[key] > b[key]
if (a[key] > b[key]) return 1
else if (a[key] < b[key]) return -1
else return 0
} else if (sort === 'desc') {
// 倒序:a[key] < b[key]
if (a[key] < b[key]) return 1
else if (a[key] > b[key]) return -1
else return 0
}
}
}
# libs > tools.js
// @函数: 引入组件
export const lazyLoadingCop = (file) =>
require('@/view/' + file + '.vue').default
# store > module > user.js
# handleLogOut 方法微调,用户登出时清空 localStorage 中的 dynamicRouter-template 数据
// 退出登录
handleLogOut({ state, commit }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 如果你的退出登录无需请求接口,则可以直接使用下面三行代码而无需使用logout调用接口
commit('setToken', '')
commit("setAccess", []);
localSave("dynamicRouter-template", []); // 清空本地存储localStorage中的dynamicRouter
resolve();
});
},